The Intro C Dressage Test is designed for horses and riders new to the sport, focusing on basic skills in walk, trot, and canter․ It emphasizes smooth transitions and correct performance, preparing the horse for more advanced levels․ This test is part of the USDF and USEF introductory series, offering a foundation for future dressage training․
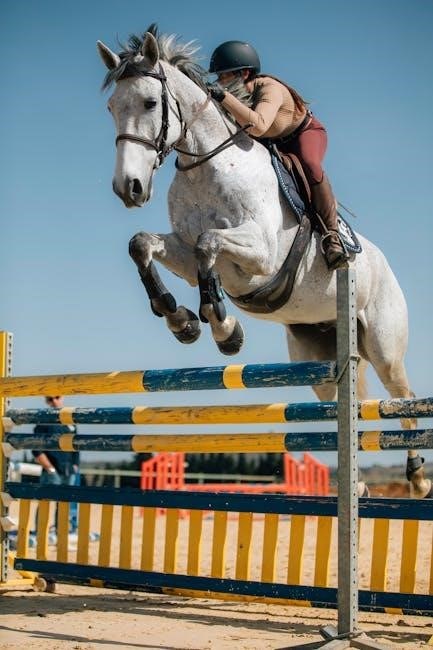

Purpose and Objectives
The purpose of the Intro C Dressage Test is to introduce riders and horses to the fundamental principles of dressage, confirming their ability to perform basic movements with clarity and precision․ Its primary objective is to assess the horse’s willingness to respond to aids and demonstrate elementary skills in walk, trot, and canter․ The test aims to evaluate smooth transitions between gaits and the horse’s ability to maintain a consistent rhythm․ Additionally, it focuses on the rider’s ability to guide the horse through a structured pattern, showcasing their understanding of basic dressage concepts․ This test serves as a foundational step, preparing both horse and rider for more advanced levels by emphasizing correct performance and clear communication between the pair․
Structure and Patterns
The Intro C Dressage Test features a clear structure with specific patterns designed to evaluate basic skills․ The test begins with an entry at working trot, rising, followed by a halt, salute, and transition to medium walk․ Patterns include serpentines, circles, and diagonal movements, testing the horse’s balance and the rider’s ability to guide smoothly․ Transitions between gaits, such as trot to canter and canter to trot, are performed through sitting trot for smoothness․ The free walk is a key component, allowing the horse to stretch and demonstrate relaxation․ The test concludes with a final centerline in trot, emphasizing precision and control․ These patterns provide a comprehensive assessment of the horse’s responsiveness and the rider’s ability to execute foundational dressage movements effectively․

Understanding the Test
Understanding the Intro C Dressage Test involves recognizing its purpose and structure․ It introduces riders and horses to dressage fundamentals, focusing on walk, trot, and canter․ Smooth transitions and correct execution of movements are emphasized, preparing for higher levels․ The test evaluates the horse’s obedience and the rider’s ability to guide through precise patterns and transitions․ By mastering these elements, participants build a solid foundation for future dressage training and competition․
Key Movements and Requirements
The Intro C Dressage Test requires riders to demonstrate proficiency in walk, trot, and canter; Key movements include working trot rising, transitions, halt, salute, free walk, and canter․ All trot work is performed in a rising trot, while transitions between trot and canter may occur through a sitting trot for smoothness․ The free walk is a critical movement, showcasing the horse’s ability to stretch and relax․ Canter work emphasizes balance and rhythm․ Riders must maintain correct posture and use subtle aids to guide the horse through patterns․ The test evaluates the horse’s obedience, balance, and responsiveness to aids, ensuring a strong foundation for higher-level dressage․ Proper execution of these movements is essential for a successful performance․
Transitions and Gaits
Transitions between gaits in the Intro C Dressage Test are crucial for assessing the horse’s responsiveness and the rider’s ability to communicate clearly․ Riders must perform smooth transitions from trot to canter and canter to trot, which may be executed through a sitting trot to ensure fluidity․ The trot work is done in a rising trot, promoting balance and engagement․ The canter is expected to be rhythmic and well-balanced, with clear transitions that demonstrate the horse’s willingness to obey aids․ A halt and salute are also required, showcasing the horse’s ability to stand immobile and attentive․ Properly executed transitions highlight the horse’s training and the rider’s skill, contributing significantly to the overall score․ These elements are fundamental in establishing a solid foundation for higher-level dressage movements․
Key Elements of the Test
The Intro C Dressage Test emphasizes rising trot, smooth transitions, and free walk execution, assessing the horse’s ability and rider’s skill in fundamental dressage elements․
Trot Work and Rising Trot
In the Intro C Dressage Test, trot work is performed in rising trot, emphasizing balance and engagement․ Riders must maintain a steady rhythm, demonstrating the horse’s ability to move freely and respond to aids․ The rising trot is crucial for developing the horse’s strength and suppleness, while also assessing the rider’s ability to sit securely and communicate effectively․ Smooth transitions into and out of trot are essential, showcasing the horse’s obedience and the rider’s coordination․ This section evaluates the fundamental skills necessary for progressing in dressage, ensuring both horse and rider are prepared for more complex movements in higher-level tests․ Correct execution of trot work lays the foundation for future success in dressage training and competition․
Transitions Between Gaits
Transitions between gaits in the Intro C Dressage Test are crucial for evaluating the horse’s responsiveness and the rider’s ability to communicate clearly․ Smooth transitions from trot to canter and canter to trot are required, with the option to perform them through a sitting trot for a seamless execution․ These transitions assess the horse’s balance, willingness, and readiness to obey aids․ Proper timing and subtlety in the rider’s aids ensure the horse remains calm and focused․ The test emphasizes the importance of maintaining rhythm and poise during gait changes, which are foundational skills for higher-level dressage․ Smooth transitions demonstrate the horse’s training and the rider’s ability to guide it effectively, showcasing their partnership and preparation for more advanced movements․ This section highlights the horse’s ability to adapt and perform accurately under gentle direction․

Free Walk and Its Execution
The free walk is a key component of the Intro C Dressage Test, allowing the horse to stretch and move naturally while maintaining a rhythmic four-beat gait․ It is typically performed along the long side of the arena, giving the horse ample space to demonstrate relaxation and ground cover․ The rider should maintain light contact with the reins, enabling the horse to stretch its head and neck freely․ This movement assesses the horse’s ability to move comfortably and willingly, showcasing its natural cadence and willingness to accept the rider’s subtle aids․ The free walk highlights the horse’s relaxation and trust in the rider, emphasizing the importance of clear and gentle communication between the two․ Proper execution of the free walk reflects the horse’s training and readiness for more advanced movements․ The judge evaluates the horse’s ability to maintain a steady, unrestricted walk, demonstrating its understanding of the aids and overall willingness to perform․ The free walk not only tests the horse’s physical ability but also its mental connection with the rider, proving it is a fundamental yet essential part of the Intro C Test․
Scoring and Judging Criteria
The Intro C Dressage Test is scored on a scale of 0 to 10, with each movement evaluated for accuracy, balance, and the horse’s willingness to perform smoothly․
How the Test is Scored
The Intro C Dressage Test is scored on a scale of 0 to 10, with each movement evaluated for accuracy, balance, and the horse’s willingness to perform smoothly․ Judges assess the quality of gaits, transitions, and overall harmony between horse and rider․ Movements such as trot work, canter transitions, and free walk are scored individually, with penalties for errors like resistance or loss of rhythm․ The test emphasizes correct execution and adherence to the pattern, rewarding clear communication and partnership․ The final score reflects the horse and rider’s ability to demonstrate elementary dressage skills effectively, providing a foundation for progression to higher levels․
Preparing for the Test
Preparation involves consistent practice of the test pattern, focusing on smooth transitions and correct execution of movements․ Understanding the test layout and timing is crucial for success․
Training Tips and Exercises
Mastering the rising trot is essential, as all trot work in the Intro C test must be performed in this style․ Practice smooth transitions between gaits, focusing on clarity and precision․ Regularly rehearse the test pattern to build familiarity and confidence․ Incorporate exercises that improve your horse’s responsiveness to aids, such as leg yields and serpentines, to enhance suppleness and balance․ Free walk drills can help develop a relaxed and ground-covering stride․ Work on maintaining a calm and focused demeanor, as this directly impacts your horse’s performance․ Seek guidance from an experienced instructor to refine your skills and address any challenges․ Consistent practice and positive reinforcement will help you and your horse excel in the test․
The Intro C Dressage Test provides a foundational platform for horse and rider, emphasizing basic skills and preparation for higher-level dressage competitions․ It is essential for building a strong foundation in dressage training․
Importance of the Intro C Test in Dressage Training
The Intro C Dressage Test plays a pivotal role in establishing a solid foundation for both horse and rider․ It introduces fundamental skills such as smooth transitions, balance, and coordination, which are essential for progression in dressage․ By focusing on walk, trot, and canter, the test ensures that the horse develops proper movement and responsiveness to aids․ This test also serves as a stepping stone for advancing to higher-level competitions, making it a crucial part of early dressage training․
Mastering the Intro C Test builds confidence and reinforces correct habits, which are vital for tackling more complex movements in the future․ It is a cornerstone for any dressage training program, emphasizing the importance of precision and harmony between horse and rider․

























